Introduction
As the world’s population continues to grow, so does the demand for energy. With the increasing awareness of the negative impact of traditional energy sources on the environment, the need for cleaner and more sustainable energy options has become paramount. This has led to the development of solar energy as a viable alternative, and advancements in solar panel technology are making it more accessible and cost-effective than ever before.
History of Solar Energy
Solar energy has been harnessed for centuries, with the first recorded instance dating back to the 7th century B.C. in China, where mirrors were used to concentrate sunlight for heat. The modern solar panel, however, was not developed until the mid-20th century, and it wasn’t until the 1970s that it began to gain popularity. Today, solar panels are used all over the world, with China and the United States leading the way in solar panel production.
Advancements in Solar Panel Technology
- Thin-film solar panels
- Bifacial solar panels
- Perovskite solar cells
- Organic photovoltaic cells
- Concentrated solar power
Thin-film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are a newer technology that uses much less material than traditional solar panels, making them more affordable and easier to install. They are also more flexible, making them ideal for use on curved surfaces, and can be made transparent for use in windows.
Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels have the ability to generate electricity from both sides of the panel, increasing their efficiency. They are also able to capture light reflected off the ground, making them ideal for use in areas with high albedo.
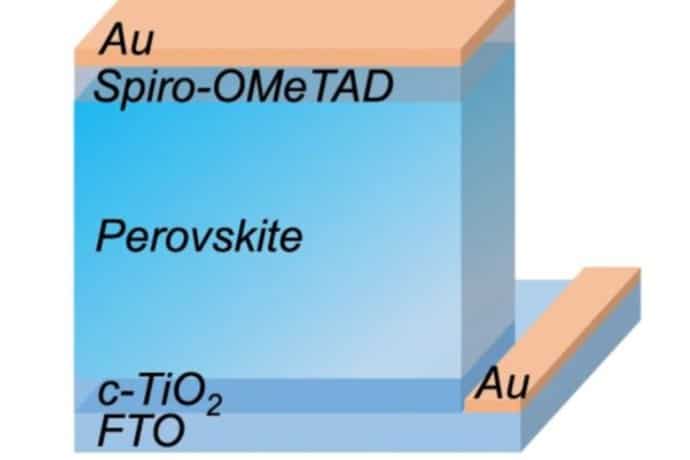
Perovskite Solar Cells
Perovskite solar cells are a newer technology that has shown great promise in recent years. They are made from a synthetic material that is cheap and easy to produce and have the potential to be much more efficient than traditional silicon solar cells.
Organic Photovoltaic Cells
Organic photovoltaic cells are made from organic materials, making them much cheaper and more environmentally friendly than traditional solar cells. They are also more flexible and can be made transparent, making them ideal for use in windows.
Concentrated Solar Power
Concentrated solar power uses mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, which is then used to generate electricity. This technology has the potential to be much more efficient than traditional solar panels but is currently more expensive and less widely used.
What’s to Come in Solar Panel Technology
- Improved efficiency
- Increased durability
- Reduced costs
- More versatile applications
Improved Efficiency
Advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes are leading to the development of solar panels that are much more efficient than current models. This means that they will be able to generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight, making them more cost-effective.
Increased Durability
Solar panels are exposed to the elements 24/7, and as such, they need to be able to withstand extreme temperatures, high winds, and heavy rain. Newer solar panels are being developed that are much more durable than current models, ensuring that they will last for many years without needing to be replaced.
Reduced Costs
The cost of solar panels has been decreasing steadily over the past few decades, and this trend is expected to continue. Advancements in manufacturing processes, as well as increased competition, are leading to lower costs for consumers.
More Versatile Applications
As solar panel technology continues to evolve, it is becoming more versatile and applicable to a wider range of uses. This includes everything from powering homes and businesses to powering transportation and even space exploration. This versatility will make solar energy an even more attractive option for those looking to reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources.
The Benefits of Solar Energy
- Environmental benefits
- Financial benefits
- Energy independence
Environmental Benefits
Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution. This means that it does not contribute to climate change or harm human health.
Financial Benefits
Investing in solar energy can provide a significant return on investment over time. Not only can it help reduce energy bills, but it can also increase the value of a property and provide long-term savings.
Energy Independence
Solar energy can provide energy independence for individuals, businesses, and even entire countries. By producing their own energy, they are not reliant on traditional energy sources that may be subject to price fluctuations or supply disruptions.
Challenges Facing Solar Energy
- Cost
- Storage
- Efficiency
Cost
While the cost of solar panels has been decreasing, they are still more expensive than traditional energy sources. This can make it difficult for individuals and businesses to invest in solar energy, especially in countries where government subsidies and incentives are limited.
Storage
One of the biggest challenges facing solar energy is storage. Solar panels only produce energy during the day, which means that it needs to be stored for use at night or during cloudy days. Current battery technology is not yet advanced enough to store large amounts of energy for long periods of time, making it a challenge for solar energy to replace traditional energy sources entirely.
Efficiency
While advancements in solar panel technology have increased efficiency, it is still not as efficient as traditional energy sources. This means that more solar panels are needed to produce the same amount of energy as a traditional power plant, which can be expensive and take up a lot of space.
Conclusion
The future is bright for solar energy, with advancements in technology making it more accessible and cost-effective than ever before. While there are still challenges facing solar energy, such as cost and storage, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and consume energy. As we continue to invest in and develop solar energy, we will be able to create a cleaner and more sustainable world for future generations.
FAQs
| Q1:How do solar panels work? |
| Solar panels work by capturing the energy from sunlight and converting it into electricity. |
| Q2:How long do solar panels last? |
| Most solar panels come with a warranty of 25-30 years, but they can last much longer with proper maintenance. |
| Q3:Can solar energy be used at night? |
| Solar energy can be used at night, but it needs to be stored in batteries or other storage systems during the day to be used later. |
| Q4:Are solar panels affordable for the average person? |
| The cost of solar panels has been decreasing steadily, making them more affordable for the average person. However, government subsidies and incentives may be necessary to make them more accessible. |
| Q5:How much energy can solar panels produce? |
| The amount of energy that solar panels can produce depends on a variety of factors, including the size of the panels and the amount of sunlight they receive. On average, a 5-kilowatt solar panel system can produce around 7,000-8,000 kilowatt-hours per year. |







