As solar energy continues to gain popularity, on-grid solar systems have become a common choice for homeowners looking to embrace renewable energy. These systems connect directly to the local electricity grid, offering unique benefits and some challenges. Below, we’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of on-grid solar systems to help you make an informed decision.
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
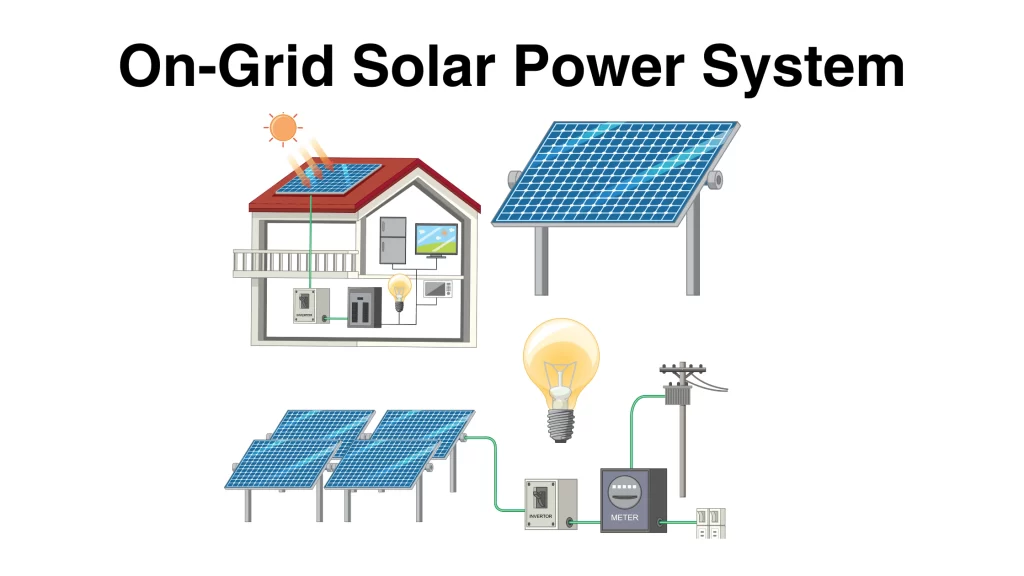
An on-grid solar system, also known as a grid-tied solar setup, is a renewable energy solution directly connected to the public electricity grid. It allows homes and businesses to produce clean energy using solar panels while maintaining a reliable link to traditional grid power. The system includes solar panels, an inverter, and a bi-directional meter, enabling users to utilize solar energy during the day, send surplus power back to the grid, and draw electricity from the grid when solar production is insufficient.
Key Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Systems
The primary difference between on-grid and off-grid systems lies in their reliance on the electricity grid. On-grid systems stay connected to the grid, allowing for two-way energy flow and eliminating the need for costly battery storage. In contrast, off-grid systems operate independently, relying entirely on solar energy and battery storage for power.
On-grid systems are more cost-effective and straightforward, leveraging the grid as a backup power source. Off-grid systems, however, require significant investment in batteries and additional equipment, making them more complex and suitable for areas without grid access.
By choosing an on-grid solar system, users can enjoy a reliable power supply, reduced electricity bills, and the flexibility of grid support when solar production fluctuates.
How Does an On-Grid Solar System Work?
An on-grid solar system integrates solar energy production with the public electricity grid to provide a seamless and efficient energy solution. Solar panels installed on your property capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. This DC power is then sent to an inverter, which transforms it into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for use in homes and businesses.
The solar-generated AC electricity powers your property, significantly reducing your dependency on grid electricity. Any surplus energy produced by the system is exported to the public grid, recorded by a bi-directional meter. Many utility companies offer net metering, allowing you to earn credits for this excess energy, offsetting future electricity costs.
When solar production is low, such as during cloudy days or at night, your property automatically draws power from the grid to ensure a continuous electricity supply. This smooth transition eliminates the need for battery storage, making on-grid systems cost-effective and user-friendly.
For safety purposes, the system shuts down during power outages to prevent sending electricity into the grid, which could endanger repair workers. Many modern systems come with monitoring tools that let users track their energy production and consumption, enabling better energy management.
In summary, an on-grid solar system works by capturing solar energy, converting it for immediate use, sharing excess with the grid, and drawing power from the grid as needed, offering a sustainable and efficient energy solution.
Key Components of an On-Grid Solar System
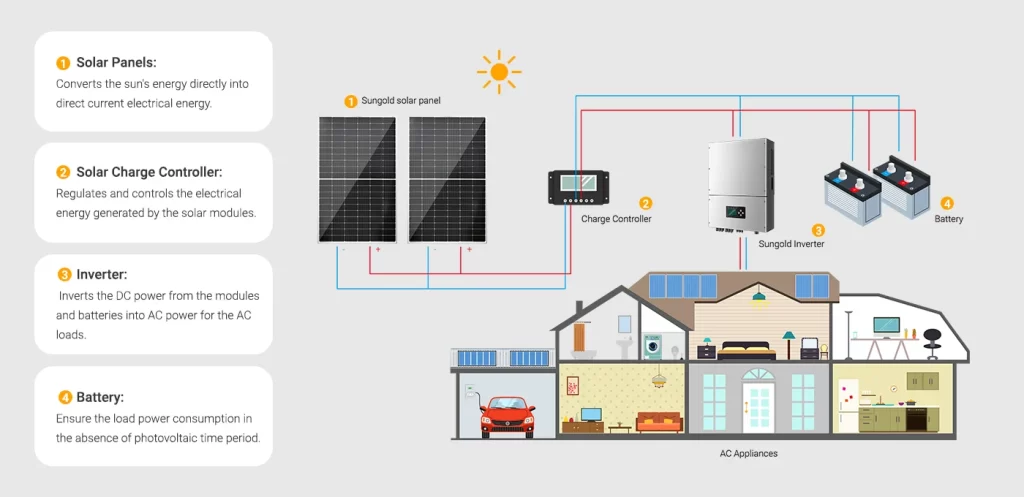
Installing an on-grid solar system involves several components and steps to ensure efficient energy production and integration with the grid. Each component plays a crucial role in generating, converting, and distributing electricity, while also maintaining system safety and reliability.
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
- Inverter: Transforms DC electricity into AC electricity for household use and grid export.
- Mounting Structure: Secures solar panels to the roof or ground.
- Electrical Wiring: Connects system components and links the solar system to the grid.
- Bi-Directional Meter: Tracks electricity flow to and from the grid, facilitating net metering.
- Monitoring System: Provides real-time data on system performance and energy usage.
Advantages of On-Grid Solar Systems
Significant Savings on Electricity Bills
One of the most attractive benefits of on-grid solar systems is their ability to reduce electricity costs drastically. By generating your power, you minimize your reliance on utility companies and their fluctuating energy rates. Many households see their monthly utility bills decrease by up to 90%, depending on system size and energy usage. Over time, these savings can offset the initial installation costs, making on-grid solar a cost-effective long-term investment.
For example, in areas with high electricity rates, such as California or New York, solar users can save hundreds of dollars per month, translating to thousands of dollars in savings annually. This financial advantage grows even further as electricity rates continue to rise globally.
Earning Through Excess Power (Net Metering)
On-grid solar systems are designed to connect directly to the local electricity grid, enabling homeowners to participate in net metering programs. This arrangement allows you to send any surplus energy produced by your solar panels back to the grid. In return, you receive credits or payments from your utility provider, effectively turning your home into a mini power station.
For instance, when solar production exceeds your household’s energy consumption on sunny days, the extra energy is exported to the grid. At night or on cloudy days, when your solar panels generate less energy, you can use the credits earned to draw power from the grid at a reduced or even zero cost. This dynamic ensures no energy is wasted and maximizes the financial return on your solar investment.
Lower Initial Investment Costs
Compared to off-grid solar systems, on-grid systems are more affordable upfront because they don’t require costly battery storage. Often used in off-grid setups, batteries can account for 30–40% of the total system cost. By eliminating this component, on-grid systems become a more accessible option for homeowners.
The lower upfront cost is particularly appealing to those who want to adopt solar energy without the financial burden of additional equipment. As solar panel prices continue to decrease globally, on-grid systems remain an economical choice for many.
Government Incentives
Governments worldwide have implemented programs to encourage solar adoption, recognizing its environmental and economic benefits. These incentives can significantly reduce the cost of installing an on-grid solar system.
For example, in the United States, homeowners can take advantage of the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which allows them to claim 30% of their installation costs as a tax credit. Many states and local governments offer additional incentives, such as rebates, property tax exemptions, or grants, further lowering the financial barriers to solar adoption.
In Europe, countries like Germany and Spain have introduced feed-in tariffs that reward solar users for the energy they contribute to the grid, while Australia offers generous solar rebate schemes.
Increased Property Value
Installing solar panels can enhance your property’s value, making it more attractive to potential buyers. Studies have shown that homes with solar energy systems typically sell at a premium compared to similar properties without solar installations.
This added value stems from the promise of lower electricity bills, reduced environmental impact, and energy independence. Buyers see solar-equipped homes as modern, energy-efficient, and aligned with sustainable living trends. In competitive real estate markets, having an on-grid solar system can make your property stand out and lead to faster sales.
Environmentally Friendly
On-grid solar systems contribute significantly to environmental conservation by reducing reliance on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. By harnessing clean, renewable solar energy, these systems help decrease the overall carbon footprint of electricity generation.
Additionally, solar energy production avoids pollutants such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which are harmful to human health and the environment. This cleaner energy source improves air quality and fosters healthier communities.
On-grid systems also play a vital role in transitioning the energy grid toward renewable sources. By integrating solar energy into the grid, they support the development of a more
Disadvantages of On-Grid Solar Systems
Dependency on the Grid
A critical drawback of on-grid solar systems is their reliance on the local electricity grid. While they generate power during the day, these systems shut down automatically during grid outages for safety reasons. Without a backup battery system, you won’t have power during a blackout, even if your solar panels are producing energy.
This dependency can be particularly problematic in areas prone to frequent or prolonged power outages. To mitigate this issue, some homeowners choose to invest in hybrid systems, which combine on-grid solar with battery storage. However, this significantly increases the initial cost of the system.
Weather-Dependent Performance
The efficiency of on-grid solar systems is directly tied to the availability of sunlight. On cloudy or rainy days, as well as during shorter daylight hours in winter, solar panels produce less electricity. This means you may need to rely more on grid power during these periods, potentially reducing your savings.
For instance, in regions with long winters or heavy monsoon seasons, the reduced output from solar panels can be significant, leading to higher electricity bills during these months. Advanced solar technology, such as high-efficiency panels or bifacial panels, can partially offset these limitations, but they come at a premium cost.
Grid Connection Challenges
Connecting your solar system to the grid can sometimes be complicated by local regulations, infrastructure limitations, or additional costs.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Some areas have strict permitting processes or require extensive documentation before allowing grid connection.
- Infrastructure Limitations: In rural or remote locations, grid infrastructure may not be robust enough to handle the additional input from solar systems, leading to delays or higher connection costs.
- Fees and Charges: Utility companies may impose fees for connecting your system to the grid or charge additional rates for net metering services.
These challenges can increase the time and cost of installation, making the process less straightforward than it might initially appear.
Maintenance Requirements
Although on-grid solar systems are generally low-maintenance, they do require periodic care to ensure optimal performance.
- Cleaning: Dust, dirt, leaves, and bird droppings can accumulate on solar panels, reducing their efficiency. Regular cleaning is essential, especially in areas prone to pollution or heavy dust.
- Inspections: Over time, components such as inverters or mounting structures may need checking or replacement to ensure the system operates safely and efficiently.
- Repairs: While rare, issues like microcracks in panels or wear and tear on wiring can occur, necessitating professional repairs.
For most homeowners, maintenance is not overly burdensome, but it does require time, effort, and sometimes additional costs.
Long-Term Efficiency Decline
Solar panels are designed to last for 25–30 years, but their efficiency gradually decreases over time. On average, panels lose about 0.5%–1% of their efficiency annually due to degradation.
This means that after 20 years, your panels might operate at only 80%–90% of their original capacity. While this decline is not drastic, it can impact the overall energy production and financial returns of your system in the long run. Advanced technologies, such as premium monocrystalline panels, tend to have slower degradation rates, but they are also more expensive upfront.

FAQ: On-Grid Solar Systems
How do on-grid solar systems benefit the environment?
On-grid solar systems reduce reliance on fossil fuels, helping lower greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, solar energy production avoids harmful pollutants, improving air quality and fostering healthier communities.
What government incentives are available for on-grid solar systems?
Governments often provide financial incentives, including tax credits, rebates, and grants. For example, U.S. homeowners can claim a 30% federal tax credit, and additional incentives may be available at the state and local levels.
How does net metering work?
Net metering allows homeowners to receive credits for excess electricity sent to the grid. These credits offset future energy consumption, helping you save on electricity bills during low-production periods, such as at night or on cloudy days.
What is the typical return on investment (ROI) for on-grid solar systems?
On average, the ROI for on-grid solar systems in the U.S. is around 10%, with payback periods ranging from 5 to 9 years, depending on installation costs, energy savings, and available incentives.
How do on-grid systems compare to traditional energy sources in cost?
While the initial investment in solar may be high, on-grid systems can lead to long-term savings by reducing energy bills. Many homeowners experience a 50% or greater reduction in electricity costs, making solar a cost-effective alternative over time.
Is an On-Grid Solar System Right for You?
The decision to install an on-grid solar system depends on several factors:
- Local Climate: Sunny regions yield higher energy production.
- Energy Consumption: High-energy users benefit most.
- Incentives: Government subsidies can lower costs.
- Grid Stability: Frequent outages may necessitate a battery backup.
On-grid solar systems offer a balanced solution for homeowners seeking renewable energy with lower upfront costs and potential long-term savings. However, assessing your energy needs and local conditions is crucial to making the right choice.
Conclusion
On-grid solar systems provide a host of advantages, including reduced electricity bills, government incentives, and environmental benefits. However, grid dependency and weather-related production variability are key considerations.
By understanding both the pros and cons, as well as the answers to common questions, you can make an informed decision about whether an on-grid solar system is the right fit for your home. Take the step toward renewable energy and enjoy the benefits of a cleaner, more sustainable future.