I will introduce the topic of connecting batteries in series vs parallel from a practical perspective. Imagine you’re planning an outdoor adventure, packing up a tent, a portable power station, and other gear, and driving to a beautiful, remote spot for a three-day, two-night trip. You might feel overwhelmed by the various parameters of batteries. Searching online for information often leads to articles that use technical jargon to explain other technical terms, leaving you more confused. This seems contradictory—if someone understood all those terms, they wouldn’t need to read those articles, right? This article is for beginners, especially those looking to try outdoor camping without diving deep into technical details.
How to Connect Batteries in Series or Parallel
Let’s recall some basic science lessons from middle school. Our teachers taught us that when connecting multiple batteries with wires, connecting the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of another is called a series connection. Connecting positive to positive and negative to negative is called a parallel connection. This might sound abstract, but it’s easier to understand with a visual representation.
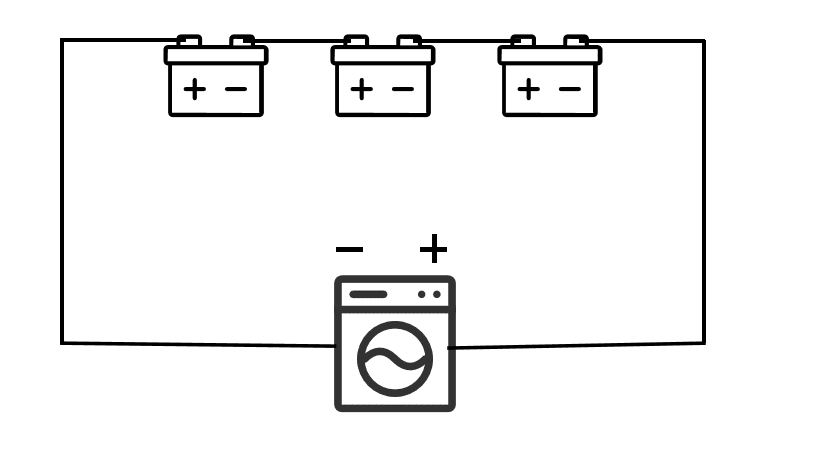
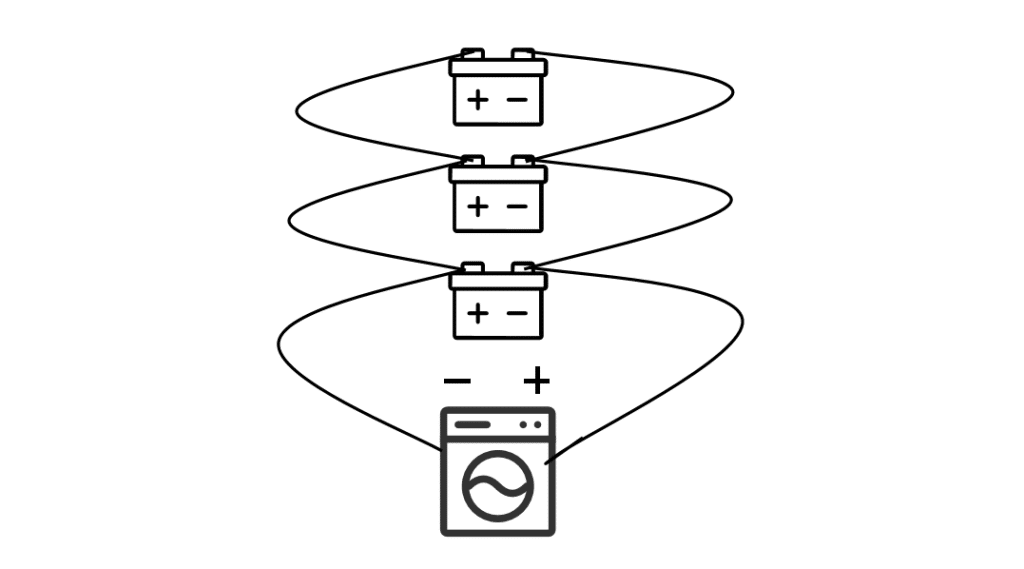
What happens When Batteries in Series vs Parallel
When batteries are connected in series, they provide higher voltage. For instance, connecting two 12V batteries in series gives you a 24V battery pack. In contrast, batteries in parallel provide higher total capacity (Ah), but the voltage remains the same—two 12V batteries in parallel still provide 12V. In a series-connected battery pack, the current is the same throughout, meaning if one battery fails or has reduced capacity, the overall performance of the pack decreases significantly, like a barrel that holds water only as high as its shortest plank. In a parallel-connected battery pack, it’s like merging several side roads into a main road. If one battery fails, the others can still supply power, and the pack continues to function.
When to Use Series or Parallel Connections?
Many articles pose this question, but the answer becomes apparent once you understand the characteristics of series and parallel connections: use series for higher voltage and parallel for higher capacity. Check the labels on your devices to determine their voltage and capacity requirements. While series and parallel connections have other characteristics, this guide focuses on providing beginners with the simplest and quickest way to get started. Remember this rule of thumb for choosing between series and parallel connections.
Important Safety Tips
At this point, I should explain various battery types, parameters, and characteristics to illustrate when you can safely connect batteries in series or parallel and when you should avoid it. However, this is a quick practical guide for beginners, so I’ll get straight to the advice:
Buy two identical batteries!
You might recall your science teacher advising against mixing old and new batteries in a TV remote. The same principle applies to rechargeable batteries. Mixing different batteries can cause issues. Understanding the specifics requires significant effort, so for a beginner looking for simplicity, buying two identical batteries is the best choice. This avoids compatibility problems altogether. If you plan to stay outdoors longer, consider buying three batteries or a portable solar panel to recharge your batteries. This way, you can use it during your trip and at home, making it more cost-effective than buying an extra battery for just a few days.
Conclusion
In conclusion of Batteries in Series vs Parallel, series connections increase voltage, parallel connections increase capacity, and different batteries should not be connected together. For simplicity, buy one large battery or two identical batteries. If you want to understand the changes that occur in batteries when connected in series or parallel from a professional perspective, you can refer to more detailed articles.







