As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy, many homeowners are considering solar panels for their homes. A common question that arises is: How many solar panels do I need to power my house? This blog will explore the factors that influence the number of solar panels required, helping you make an informed decision about your solar energy system.
.jpg)
Understanding Your Energy Needs
The first step in determining how many solar panels you need is to assess your household’s energy consumption. On average, a typical U.S. home consumes about 877 kWh per month, which translates to approximately 10,500 kWh annually. However, this figure can vary significantly based on several factors:
- Home Size: Larger homes generally consume more electricity.
- Family Size: More occupants typically lead to higher energy usage.
- Appliance Efficiency: The type and efficiency of appliances can greatly impact overall consumption.

Average Number of Solar Panels Required
Based on average energy consumption, most homes will require between 15 and 30 solar panels to offset their electricity usage fully. Here’s a quick overview of estimated panel requirements based on home size:
| Home Size | Estimated Number of Panels |
|---|---|
| 800 sq ft | 8 to 10 panels |
| 1,000 sq ft | 10 to 12 panels |
| 1,200 sq ft | 12 to 14 panels |
| 1,500 sq ft | 15 to 18 panels |
| 2,000 sq ft | 20 to 24 panels |
| 2,500 sq ft | 25 to 28 panels |
| 3,000 sq ft | 28 to 32 panels |
These estimates are based on solar panels with an output of around 300 to 400 watts each, which is common in today’s market.
Key Factors Influencing Solar Panel Requirements
Several factors can affect the total number of solar panels needed for your home:
Electricity Consumption
Your monthly electricity bill provides a clear picture of your energy usage. To accurately assess how many solar panels you need, consider reviewing your utility bills over the past year to identify any seasonal variations in usage.
Peak Sunlight Hours
The amount of sunlight your location receives is crucial in determining solar panel efficiency. Areas with more sunny days will require fewer panels compared to regions with frequent cloud cover. For instance:
- States like Arizona may receive up to 210 peak sun hours monthly.
- Conversely, states like Alaska might only get about 90 peak sun hours monthly.
Solar Panel Efficiency
The efficiency rating of the solar panels you choose will also impact how many you need. Higher efficiency panels convert more sunlight into electricity, potentially reducing the total number required for your system.
Calculating Your Solar Panel Needs
Determining how many solar panels you need for your home depends on your monthly energy usage, the average peak sunlight hours in your location, and the wattage of the solar panels you plan to use. You can calculate this with a simple formula:
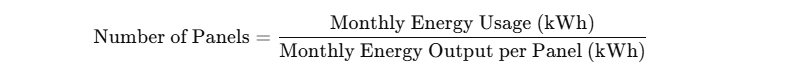
To calculate the Monthly Energy Output per Panel, use the following equation:
Monthly Energy Output per Panel=Panel Output (kW)×Peak Sun Hours (hours per day)×30
Example:
If your home uses 900 kWh per month, your location receives an average of 5 peak sun hours per day, and each panel has a capacity of 300 watts (0.3 kW):
- Daily energy output per panel:
0.3 kW×5 hours=1.5 kWh/day - Monthly energy output per panel:
1.5 kWh/day×30 days=45 kWh/month - Number of panels needed:
900 kWh/month/45 kWh/month=20 panels
So, to meet your energy needs, you would require 20 solar panels.
Solar Panel for Home Calculator
To make things easier, use the solar panel calculator below to estimate the number of panels you need. Just enter your monthly energy usage, average peak sun hours, and the wattage of your panels to get an accurate result tailored to your specific needs.
Understanding Solar Panel Output
To illustrate further, let’s consider a practical example: If you have a 1,000 sq ft home and decide on using 10 solar panels, each with a capacity of 375 watts, the total wattage would be approximately 3,750 watts (or 3.75 kW). Assuming an average level of sun exposure on your roof, you can expect an annual energy production that is about 1.25 times the total wattage of your system. Therefore:
This figure helps in understanding how a solar panel system can cover a home’s yearly energy usage.
Cost Considerations
When planning for solar panel installation, it’s essential to consider costs as well. The price of solar panels has decreased significantly over recent years, making them more accessible than ever. On average:
- The cost per watt ranges from $0.50 to $0.70.
- For instance, if you purchase a 350-watt panel, it could cost around $175.
For a home with an estimated requirement of 20 panels, the total installation cost might be around $18,000, depending on various factors such as location and available incentives.
Best Solar Panel for Your Hom
If you’re looking for the best solar panel for your home, the Sungold SGM Series should be at the top of your list. With outstanding performance, reliability, and cutting-edge technology, this solar panel is designed to meet all your energy needs, providing a clean, safe, and cost-effective solution for your home.
Key Features:
- High Efficiency: The Sungold SGM Series boasts high-efficiency output, ensuring optimal energy production even in less-than-ideal conditions.
- Durability: Built to last, these panels can withstand extreme weather conditions, including snow loads of up to 5400 Pa and wind loads of up to 2400 Pa.
- Impact Resistance: With robust construction and superior impact resistance, the SGM Series can handle harsh outdoor environments, from heavy winds to snowfall.
- Waterproof & Weatherproof: Rated IP67, the panels are fully waterproof and ready for long-term outdoor installation, making them ideal for rooftop, off-grid, RV, or boat applications.
- Ease of Installation: Designed with convenience in mind, the panels come with special mounting brackets for easy and hassle-free installation.
- Proven Quality: Tested to IEC 61215 standards, including fire resistance and visual inspections, these panels meet the highest safety and quality requirements.
Conclusion
So, How Many Solar Panels Are Needed to Power a House? On average, homeowners can expect to need between 15 and 30 solar panels for complete energy offset. Investing in solar energy not only reduces your carbon footprint but can also lead to significant savings on electricity bills over time. If you’re considering installing solar panels for your home, consulting with a professional installer can provide tailored advice based on your unique needs and circumstances.By taking these factors into account and using accurate calculations, you can confidently embrace solar power as a sustainable solution for your home while enjoying the benefits it brings. For those interested in exploring more about how many solar panels are ideal for their specific situation or seeking further assistance with installation options and costs, reaching out to local solar providers or utilizing online calculators can provide valuable insights tailored to individual needs.
FAQ: Solar Panels for Your Home
How does panel efficiency affect energy production?
Higher-efficiency panels convert more sunlight into electricity, reducing the number of panels needed. Panels today have efficiencies ranging from 15% to 22%, with new technologies improving performance.
What is the average lifespan of solar panels?
Solar panels typically last 25 to 30 years, with warranties ensuring at least 80% efficiency for 25 years. Efficiency may gradually decline, but most systems continue to generate usable energy beyond the warranty period.
How do peak sunlight hours impact solar panel installation?
Peak sunlight hours refer to when sunlight is most intense, typically midday. Locations with more peak sun hours need fewer panels. Understanding your area’s sunlight hours helps optimize panel sizing and system efficiency.
What are the costs associated with installing solar panels?
Costs vary based on factors like system size, panel type, and installation complexity. On average, a complete installation costs between $16,500 and $25,000, including equipment and labor. Financing options may affect overall costs.








