Table of Contents
- What is a Solar Carport?
- How Do Solar Carports Work?
- Key Features of Solar Carports
- Flexible Solar Carports vs. Traditional Solar Carports
- Flexible Solar Carports vs. Traditional rigid Solar Carports: A Cost-Effectiveness Comparison
- Pros and Cons of Solar Carports
- Differences Between Residential and Commercial Solar Carports
- How to Install a Solar Carport
- Policy Incentives and Cost Benefits
- Final thoughts
As renewable energy continues to transform our world, solar carports are becoming a popular solution for maximizing space while generating clean energy. These innovative structures provide shade and protection for vehicles while contributing to a more sustainable future. If you’re considering solar carports, this guide covers everything you need to know.
What is a Solar Carport?
A solar carport is a covered parking area with solar panels integrated into the structure. Unlike traditional carports that use fabric or metal roofing, solar carports feature photovoltaic (PV) panels that generate electricity. This dual-purpose design offers both renewable energy and protection for vehicles.
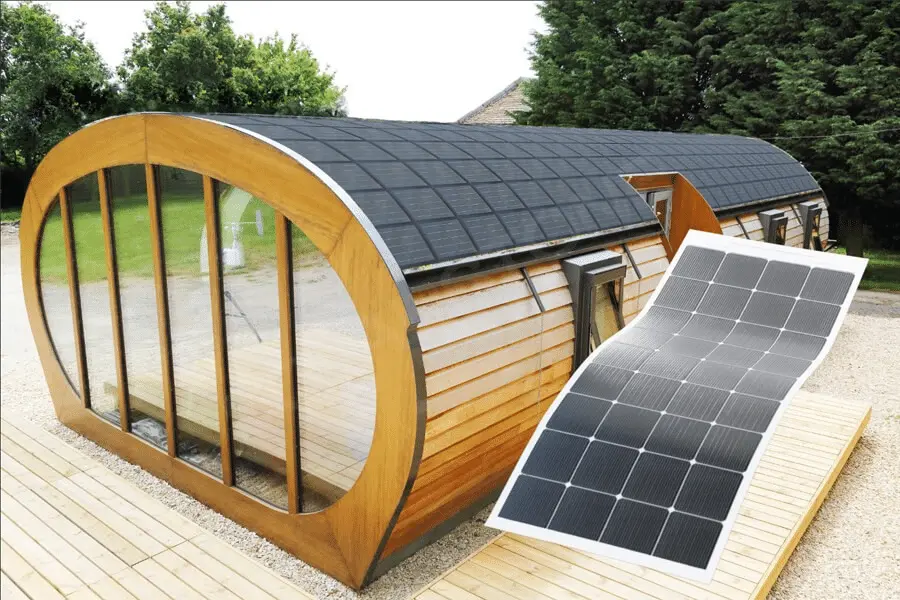

Applications:
Solar carports are versatile and can be used in various settings:
Residential: Installed in driveways or small parking lots for homes.
Commercial: Suitable for shopping centers, office complexes, and other large-scale parking spaces.
Public Infrastructure: Found in schools, airports, and parks to generate clean energy for public use
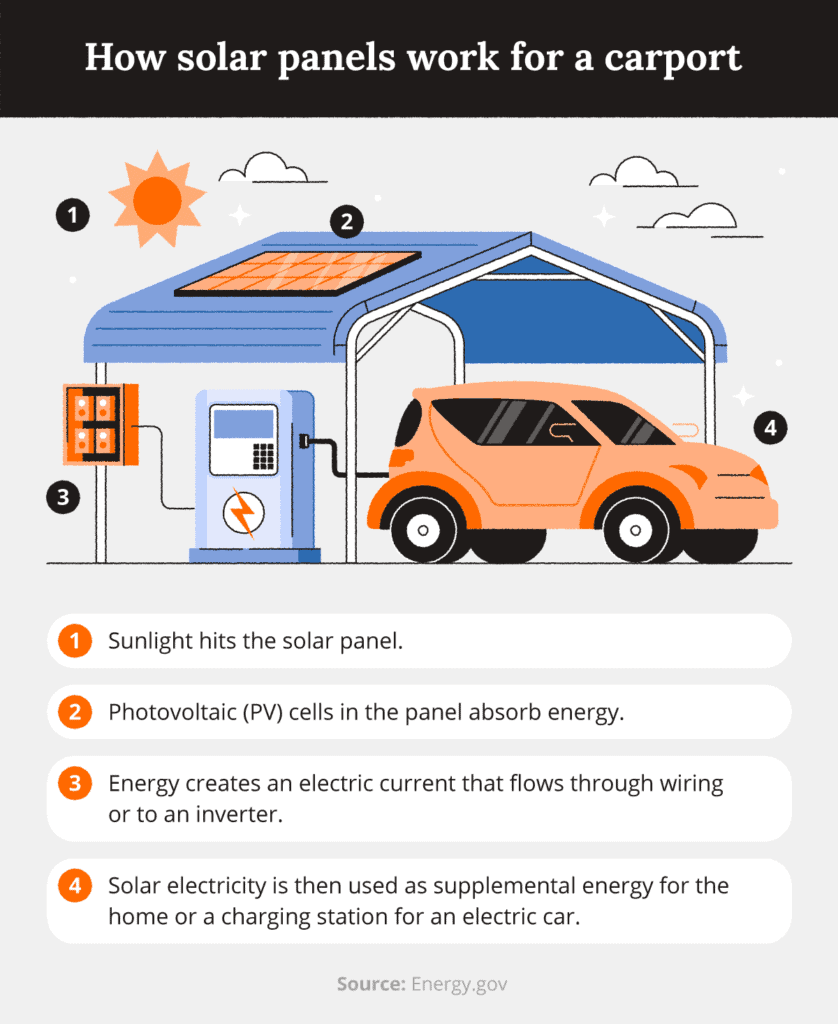
How Do Solar Carports Work?
Structure and Installation
Unlike rooftop solar systems, solar carports are ground-mounted, with panels elevated high enough to allow vehicles to park underneath. This structure ensures dual functionality: electricity generation and vehicle protection.
Power Generation Process
Solar carports capture sunlight through PV panels. The energy is converted into direct current (DC) electricity, which is then passed through an inverter to become alternating current (AC) for use in homes, businesses, or even the grid.
Comparison to Rooftop Systems
While rooftop solar panels require an existing structure, solar carports can be standalone installations. They offer flexibility in placement, making them ideal for locations with insufficient roof space.
Key Features of Solar Carports
Aesthetic Appeal:Solar carports elevate the appearance of parking spaces with their sleek, modern design, often adding visual value to a property.
Practicality and Adaptability:They serve dual purposes by providing shade and energy, and their modular design makes them adaptable to different locations and needs.
Energy Efficiency:Solar carports utilize sunlight effectively, contributing to lower energy costs and reduced carbon footprints
Long-Term Durability:Built with high-strength materials, solar carports withstand harsh weather conditions and provide power for up to 25 years.
Cost-Effectiveness:The initial investment can be offset by government incentives, energy savings, and potential revenue from selling surplus electricity.
Flexible Solar Carports vs. Traditional Solar Carports
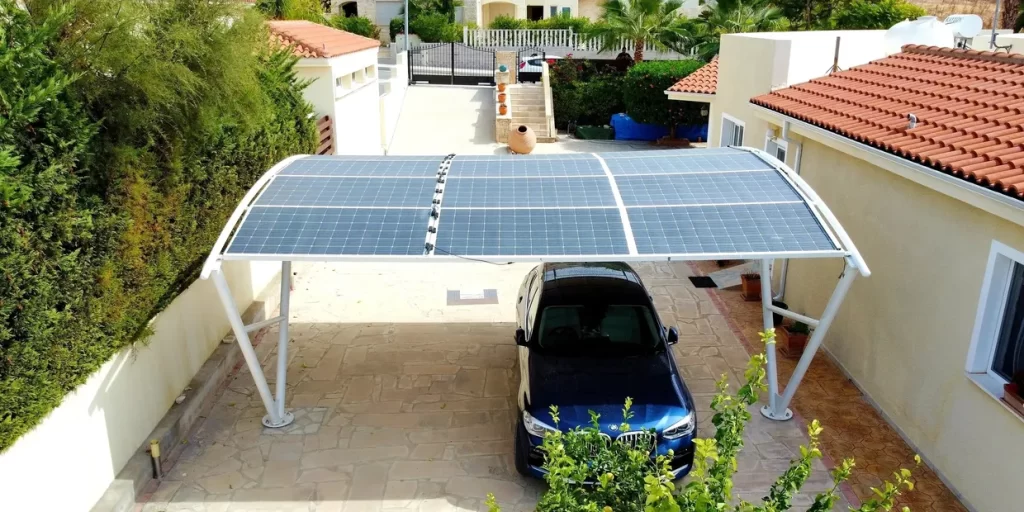
Flexible Solar Carports
Flexible solar carports use lightweight solar panels, like ETFE-coated panels, making them ideal for curved or irregular surfaces. These panels are easy to install, cost-effective, and suitable for areas with strong winds or snow.

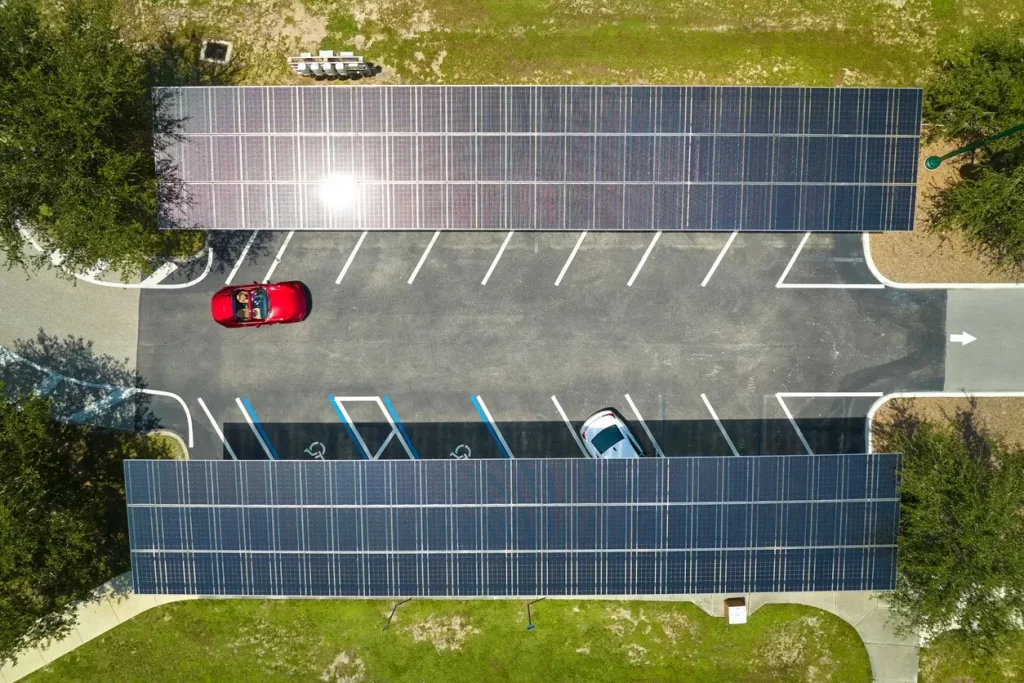
Traditional Solar Carports
Constructed with rigid solar panels, traditional carports are durable and suited for commercial and industrial applications. However, they are heavier, more costly, and require stronger support structures.

Flexible Solar Carports vs. Traditional rigid Solar Carports: A Cost-Effectiveness Comparison
When choosing a solar carport, flexibility and cost-efficiency are crucial factors to consider. Flexible solar carports offer distinct advantages over traditional glass solar carports, particularly in terms of cost savings and adaptability. Here’s a detailed breakdown of why flexible solar carports stand out:
Lower Material Costs:
Flexible solar panels are made from affordable materials like thin-film solar cells, which are cheaper to manufacture compared to the silicon-based rigid panels used in glass solar carports. This translates to significant savings in material expenses without compromising functionality.
Reduced Shipping and Installation Costs
Lightweight Design: Flexible solar panels weigh much less than traditional glass panels, making transportation more economical.
Ease of Installation: The rollable and pliable nature of flexible panels simplifies the installation process, reducing labor costs and the time needed for setup. These attributes make them particularly suited for quick deployments.
Minimal Maintenance Requirements
Due to their material properties, flexible solar panels are more resistant to wear and tear, requiring less frequent cleaning or repairs. This can significantly lower maintenance expenses over the lifetime of the carport
Greater System Adaptability:Flexible solar panels can be installed on irregular or curved surfaces, unlike rigid panels that demand flat or well-structured bases. This adaptability minimizes the need for structural modifications, saving additional costs and enabling installation in spaces where traditional panels would be impractical.
Improved Environmental Resilience
Flexible solar panels are designed to withstand extreme weather conditions, including:
Strong Winds: Their lightweight and flexible nature makes them less prone to damage during high winds
Snow Loads: Unlike fragile glass panels, flexible panels are less likely to crack or fail under heavy snow.
Flexible solar carports combine cost-effectiveness, durability, and adaptability, making them a superior choice for a wide range of applications. From reducing upfront material and installation expenses to minimizing long-term maintenance and weather-related risks, these carports represent a forward-thinking investment in sustainable energy solutions.
Pros and Cons of Solar Carports
Pros:
Efficient Space Utilization: Maximize parking areas for dual purposes.
Government Incentives: Tax credits and rebates help reduce initial costs.
EV Charging Integration: Seamlessly supports electric vehicle infrastructure.
Eco-Friendly: Reduces dependency on fossil fuels and minimizes emissions.
Cons:
Higher Initial Costs: Material and installation expenses can be significant.
Complex Installation: Requires professional expertise for safety and efficiency.
Permitting Challenges: Local regulations may extend project timelines.
Differences Between Residential and Commercial Solar Carports
Residential Solar Carports
Designed for single-family homes with smaller parking areas.
Use lightweight materials for easy customization.
Cost-effective and ideal for personal renewable energy needs.
Commercial Solar Carports
Built with robust steel bases to support larger panels
Serve large-scale parking lots, such as shopping malls or office spaces
Higher initial costs but larger energy output and financial benefits over time
How to Install a Solar Carport
Professional Installation
Most providers offer turnkey solutions, handling everything from design to installation. For grid-connected systems, professionals ensure safety and compliance with local codes.
DIY Installation
Small-scale, off-grid carports can be DIY projects. While cost-effective, DIY installations require knowledge of solar panel wiring and structural integrity. Hiring certified electricians for complex setups is recommended.

Policy Incentives and Cost Benefits
Federal Tax Credits: The U.S. offers up to a 30% tax credit on installation costs
State and Local Rebates: Additional subsidies vary by state, further reducing expenses
Long-Term Savings: Generate electricity for decades, reducing or eliminating utility bills
Final thoughts
Solar carports are a powerful innovation for those seeking to combine functionality, sustainability, and efficiency. Whether for residential or commercial use, they optimize space, support renewable energy, and enhance property value.
Explore solar carport options today and contribute to a greener, brighter future!