The growing demand for off-grid energy has driven significant technological advancements, particularly in the solar energy sector. One notable development is the n-type solar panel. These panels are made from electron-rich n-type silicon, known for their high efficiency and long lifespan. In this article, we will delve into TOPcon versus Mono PERC solar technologies, analyzing which one offers greater production efficiency and helping you evaluate whether they meet your needs.
Table of Contents
What is a TOPCon Solar Cell?
A TOPCon solar cell is a high-efficiency silicon solar cell that combines the advantages of PERC and HJT technologies, offering 5% higher efficiency than traditional cells. TOPCon stands for Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact and is currently one of the most widely used technologies in new solar cells. As a leading trend in the photovoltaic market, TOPCon solar cells are being adopted by more and more manufacturers. For example, our balcony power generation systems use TOPCon cells, ensuring maximum power output in solar modules
Advantages of N-type TOPCon
TOPCon solar cells offer several advantages over traditional solar cells, with the most notable being their higher photovoltaic conversion efficiency.
Key Highlights:
- Higher Efficiency
- Lower Temperature Coefficient
- Higher Bifacial Coefficient
- Low Capital Investment for Manufacturers
According to data from the Fraunhofer ISE Institute, TOPCon solar cells achieve efficiencies exceeding 25%, significantly higher than conventional photovoltaic modules. The temperature coefficient of traditional photovoltaic modules typically ranges between 0.4% and 0.5% per degree Celsius, while TOPCon solar modules have a slightly lower temperature coefficient, performing better at just under 0.4%. Additionally, the bifacial coefficient of TOPCon cells has been increased from the traditional 70% to 85%, resulting in an overall performance improvement of around 2% under optimal conditions.
TOPCon solar cell technology is a further optimization of PERT and PERC solar cells, requiring only two additional steps in the production process. Manufacturers need only a small investment in equipment and capital to convert production from PERC to TOPCon solar cells.
However, the manufacturing process of TOPCon technology also presents some challenges, such as differing views on boron deposition techniques, varying cleanroom requirements, and the incompatibility of current selective emitter technology with TOPCon front-side emitters. Additionally, due to the different production methods employed by manufacturers, mass production has yet to reach a unified standard.
Disadvantages of N-type TOPCon
- Challenges in Manufacturing Process: The production process is not yet fully matured.
- Increased Demand for Silver: This leads to higher prices.
- Complex Production Process: This can result in higher initial costs and potential challenges during manufacturing.
How are TOPCon Solar Cells Constructed?
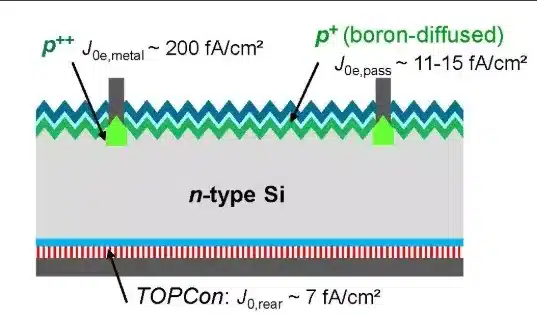
TOPCon solar modules use n-type solar cells, which are made from n-type doped silicon wafers and thus carry a negative charge. TOPCon solar cells feature rear-side passivation with a thin oxide layer, a technique that minimizes electronic defects within the cell. Additionally, they reduce the number of front-side metal contacts, thereby increasing the amount of light entering the cell and maximizing light absorption efficiency. TOPCon cells also optimize electron flow through tunnel oxide passivation technology.
In contrast, traditional solar cells have metal contacts on both the front and back, which can lead to energy losses. Moreover, these cells typically use aluminum for rear-side passivation, which is less effective compared to the oxide passivation used in TOPCon technology.
How Do TOPCon Solar Cells Work?
TOPCon solar cells enhance overall efficiency by preventing charge carriers from recombining at the rear of the cell through the elimination of direct contact between metal contact points and the silicon layer.
To prevent recombination, the surface of the solar cell is coated with a thin layer of silicon oxide. This passivation layer blocks the movement of charge carriers, but due to quantum mechanical effects, the current can overcome this barrier—a phenomenon known in physics as “tunneling.” Additionally, a heavily doped silicon layer further improves conductivity and minimizes transmission losses.
How Do PERC Solar Cells Work?
PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) solar cells are an advanced solar technology that improves photoelectric conversion efficiency by adding a passivation layer to the back of the cell. Here’s how PERC solar cells work and their benefits:
Working Principle
Photovoltaic Effect: When sunlight hits a PERC solar cell, the energy from the photons excites electrons in the silicon lattice, creating electron-hole pairs. These pairs are separated by an electric field, with electrons moving towards the positive terminal and holes moving towards the negative terminal, generating an electric current in an external circuit.
Role of the Passivation Layer: PERC cells add a passivation layer to the back of the traditional solar cell. The primary function of this layer is to reduce electron recombination, decreasing the chance of electrons and holes recombining, thereby increasing the overall efficiency of the cell.
Light Reflection and Reutilization: The passivation layer also has reflective properties, reflecting unabsorbed photons back into the silicon wafer, giving them a second chance to be absorbed and converted into electricity. This design further enhances photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Advantages
- Higher Energy Conversion Efficiency: The passivation layer reduces energy losses, significantly improving the cell’s efficiency.
- Better Low-Light Performance: PERC cells perform well in low-light conditions, making them suitable for a wide range of environments.
- Improved Temperature Stability: PERC cells maintain more stable output in high-temperature environments.
- Longer Lifespan: The optimized design extends the cell’s lifespan, providing a more durable energy solution.
TOPCon Technology Represents a Market Breakthrough for N-Type Cells
Silicon solar cells dominate the global solar cell production market, combining high efficiency, cost-effective production, and reliable lifespan. These cells are composed of two layers: an n-layer (negative charge, conductive) and a p-layer (positive charge, containing so-called “holes,” or unoccupied charges). The thickness of each layer varies, with the thicker layer (also known as the substrate) determining whether the solar cell is p-type or n-type.
In the solar industry, p-type cells have traditionally dominated the market because they are easier and cheaper to produce. However, an increasing number of photovoltaic manufacturers are now shifting towards n-type cells because they offer higher efficiency and are less susceptible to power loss.
For instance, the “initial degradation” effect commonly seen in p-type cells refers to a decrease in efficiency when sunlight first hits the cell module due to a chemical reaction within the cells. N-type cells, however, do not experience this effect, allowing solar modules to maintain their maximum output upon delivery.
Other advantages of n-type cells include reduced sensitivity to metal impurities in silicon, lower power-induced degradation (PID), and greater temperature resilience. Additionally, n-type cells have a lower temperature coefficient, meaning their performance only slightly decreases as the temperature rises.

TOPCon or PERC Cell Design Components? Both Concepts Can Simultaneously Influence the Market
Despite the impressive performance of TOPCon solar cells, PERC technology continues to dominate the market. This dominance is primarily due to the ongoing improvements in PERC cell efficiency and the continual reduction in production costs—a trend that is expected to persist for some time.
However, the market significance of TOPCon cells is increasingly rising due to their extremely high efficiency. As mass production advances, economies of scale are expected to significantly reduce costs, positioning TOPCon modules as strong contenders against PERC technology in the German market. Researchers at Fraunhofer-ISE support this view, suggesting that to ensure the economic viability of TOPCon modules, it is crucial not only to reduce manufacturing costs but also to increase production volumes to levels comparable to those of PERC cells.
Which Solar Panel Should We Use: N-Type or P-Type?
When designing a new solar module, the first decision you need to make is whether to choose N-type or P-type solar panels. When making this choice, consider your budget, energy requirements, and available installation space.
N-type solar panels are generally more expensive than P-type panels, but they are more efficient and capable of generating more electricity. Therefore, if your energy demands are high, N-type solar panels may be the better option for you. On the other hand, P-type solar panels are more affordable, and while they are slightly less efficient, they remain a cost-effective choice for typical household users.
The size of the installation space is also a crucial factor. If your available space is limited but you need higher power output, the high efficiency of N-type solar panels will be an advantage. If you have ample space and are budget-conscious, P-type solar panels can meet your needs while saving on costs.
Since 2008, Sungold Solar has been dedicated to developing high-quality solar modules. We offer a variety of options, including black, black-framed, silver, as well as glass-glass designs in half-cut, MBB, and shingle solar modules. These modules not only perform exceptionally well but also feature aesthetically pleasing designs suitable for various architectural applications. We have established long-term partnerships with many large distributors and retailers. Please contact us for the latest module products or any other photovoltaic-related inquiries. We look forward to assisting you.







