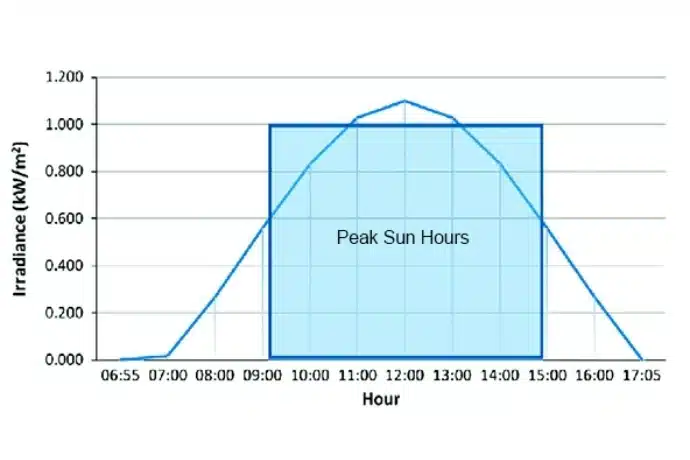
While many people think about average sun hours per day, peak sun hours are a more precise measure of solar potential. Rather than just counting the number of hours, this concept looks at the intensity of the sun’s radiation.
Peak sun hours are defined as the hour when the intensity of the sun reaches an average of 1,000 watts per square meter.
By looking at a sun hour map and analyzing how many hours of sunshine different regions receive per day, we can better plan and implement solar technology. In this guide, we’ll teach you about peak sun hours, how they differ from state to state, how they are measured, why they are important in solar decisions, and how to calculate them for your specific location.
What are peak sun hours?
“Peak sun hours” are the hours when the intensity of solar radiation (or sunlight) reaches an average of 1,000 watts of energy per square meter (or 10.5 feet). In short, peak sun hours are equivalent to 1,000W of sunlight per square meter for one hour.
Here is the math for peak sunshine hours:
1 peak sunshine hour = 1 hour of sunshine, 1000 watts per square meter = 1000 watts per square meter.
Or, 1 peak sunshine hour = 1 kW/square meter
While solar panels receive an average of 7 hours of sunlight, the average peak sunshine hours are generally around 3 or 5. Off-peak sunshine hours are the remaining time when solar panels receive sunlight but not at high intensity.
Peak Sunshine Hours by State
Due to the vast geographic area of the United States and its various climate zones, peak sunshine hours vary greatly from state to state. Below is a table and peak sunshine hour graph representing other regions.
| State | Peak Sun Hours | State | Peak Sun Hours |
| Alabama | 3.5 – 4 | Louisiana | 4 – 4.5 |
| Alaska | 2 – 3 | Maine | 3 – 3.5 |
| Arizona | 7 – 8 | Maryland | 3 – 4 |
| Arkansas | 3.5 – 4 | Massachusetts | 3 |
| California | 5 – 7.5 | Michigan | 2.5 – 3.5 |
| Colorado | 5 – 6.5 | Minnesota | 4 |
| Connecticut | 3 | Mississippi | 4 – 4.5 |
| Florida | 4 | Missouri | 4 – 4.5 |
| Georgia | 4 – 4.5 | Montana | 4 – 5 |
| Illinois | 3 – 4 | Nebraska | 4.5 – 5 |
| Indiana | 2.5 – 4 | Nevada | 6 – 7.5 |
| Iowa | 4 | New Hampshire | 3 – 3.5 |
| Kansas | 4 – 5.5 | New Jersey | 3.5 – 4 |
| Kentucky | 3 – 4 | New Mexico | 6 – 7 |
Why do peak sunshine hours vary by state and region?
Ever wondered why some states seem to be bathed in endless sunlight while others barely see any? The answer lies in the fascinating world of peak sunshine hours, which can vary dramatically from place to place.
While average daily sunshine hours give us a rough idea of sunshine hours, peak sun hours provide a more detailed picture of solar potential. These variations are influenced by several key factors:
- Latitude: States near the equator generally enjoy more peak sun hours. This is why sunshine hour maps often show southern states as having solar potential.
- Climate: Local weather patterns have a significant impact on how many hours of sunshine per day translate to peak sun hours. Cloudy coastal areas may have longer days but fewer peak sun hours than dry inland areas.
- Season: Peak sun hours fluctuate throughout the year. Northern states may have contrasting peak sun hours in the summer and winter, while southern states have more consistent peak sun hours.
- Topography: Mountains, valleys, and even city skylines can affect the amount of local sunshine, creating microclimates with varying peak sun hours within the same state.
- Atmospheric conditions: Air quality, humidity, and altitude all determine the amount of solar radiation reaching the ground, which affects peak sun hour calculations.
How does peak sun hours affect my solar panels?
First, peak sunshine hours determine the energy output of solar panels. While solar panels generate electricity throughout the day, they reach their peak efficiency during these high-intensity hours. The longer the peak sunshine hours, the greater the energy production, which can potentially save more on your electricity bill.
The peak sunshine hours in your location can also affect the size and design of your solar system. Areas with fewer peak sunshine hours may require more panels or more efficient modules to meet the same energy needs as areas with more sunshine. This factor can affect both your initial investment and the long-term payback of your solar project.
Additionally, peak sunshine hours can affect how quickly your solar investment pays back. Areas with more peak sunshine hours generally have shorter payback periods because solar panels in these areas can generate more electricity over time.
It’s worth noting that even if your area doesn’t have the highest peak sunshine hours, solar energy can still be a viable option. Advances in solar technology have made solar panels more efficient even in less-than-ideal conditions. However, knowing your local peak sunshine hours can help set realistic expectations and guide you to make better decisions on your solar journey.
By considering factors such as peak sunshine hours as well as local electricity prices and available incentives, you can make an informed decision about solar energy. Keep in mind that while peak sunshine hours are critical, they are only one piece of the solar puzzle—but understanding them can get you closer to effectively using solar.
How many peak sunshine hours do you need to use solar?
While more peak sunshine hours are generally better, there is no universal minimum requirement. Many solar experts consider 4 hours of peak sunshine per day to be a good benchmark for solar viability, but areas with less peak sunshine hours can still benefit from solar.
Your specific needs will depend on several factors:
- Local climate and shade
- Home energy consumption
- Solar panel efficiency
- Local electricity prices and solar incentives
Remember that even areas with fewer peak sunshine hours, like New Jersey or Massachusetts (4-5 hours), have a thriving solar market. Modern solar technology is getting more efficient, making solar viable in more places. Don’t let fewer peak sunshine hours discourage you.






