What Size Solar Panels Do You Need to Run Your Whole House?Solar power is rapidly becoming a top choice for homeowners looking to cut electricity costs and reduce their environmental footprint. Determining the right size for a solar power system to fully power your home requires careful consideration of key factors, such as your household’s energy usage, the amount of sunlight your location receives, and the efficiency of the solar panels you choose. This guide breaks down these essential elements and introduces tools like the Peak Sun Hours Calculator to help you plan an effective and efficient solar energy system.

Why Calculate the Size of Your Solar Power System for Home?
The goal of any home solar electricity project is not just to install as many solar panels as possible but to optimize energy production and maximize cost savings. By sizing your system accurately, you can ensure it offsets 100% of your electricity usage, effectively cutting down your reliance on grid power. Moreover, a properly sized solar panel home kit helps avoid overinvestment or underperformance, both of which could impact your financial returns.
What Factors Affect the Size of a Solar Power System for Home?
Your Home’s Electricity Consumption
The starting point for sizing a solar power system is understanding your household’s electricity usage. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average American household consumed 10,632 kWh of electricity in 2021, which equates to approximately 886 kWh per month or about 30 kWh daily. If your household consumes more or less than the national average, the size of your solar power system will need to reflect that.
Example:
· A family in the Southwest using 12,000 kWh annually will need a larger system than a smaller household in the Northeast consuming 9,000 kWh annually.
Peak Sun Hours Availability
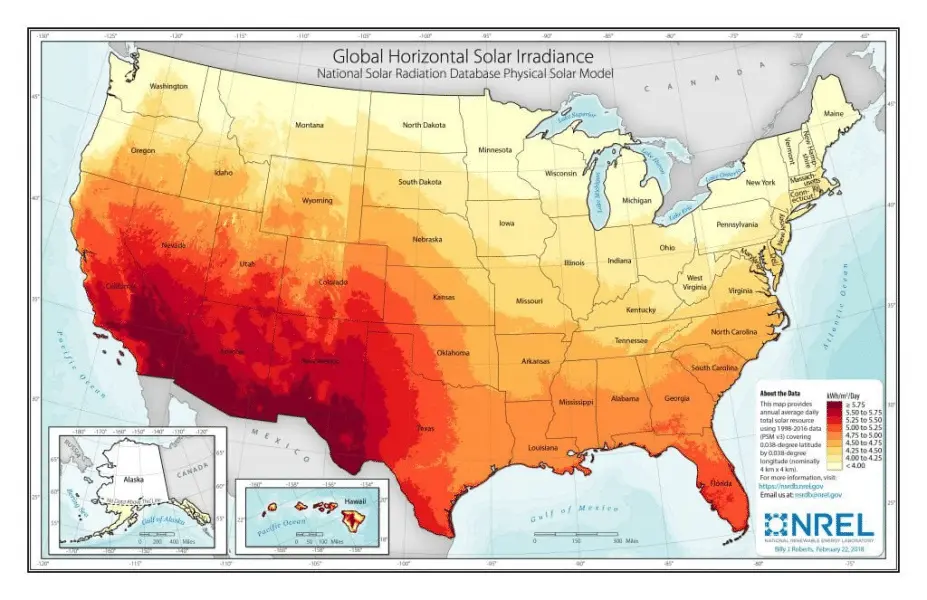
Peak sun hours refer to the number of hours in a day when sunlight intensity is strong enough to produce maximum power output from solar panels. This varies by location:
· Southwest U.S.: More than 5.75 hours per day.
· Northern U.S.: Typically fewer than 4 hours per day.
You can use a Peak Sun Hours Calculator to determine the sunlight availability for your specific location.
Solar Panel Efficiency and Wattage
Solar panels range in power ratings from 250W to 450W, with 400W being a popular choice due to its efficiency and price balance. Higher wattage panels generate more energy per square foot, meaning fewer panels are needed.
· Example Calculation:
· A 400W panel receiving 4.5 peak sun hours daily will produce approximately 1.8 kWh/day. To meet a daily usage of 30 kWh, around 17 panels would be required.
How Many Solar Panels Does the Average Home Need?
The number of panels required depends on the household’s electricity usage and the conditions outlined above. On average, a U.S. household requires between 17 and 30 panels to fully offset electricity costs. This range is based on the assumption of using high-efficiency panels and optimal sunlight conditions.
Quick Formula:
Daily Energy Usage ÷ (Panel Wattage x Peak Sun Hours) = Number of Panels Needed
Example:
A home consuming 30 kWh daily in a location with 4.5 peak sun hours and using 400W panels:
30÷(0.4×4.5)=16.6730 ÷ (0.4 × 4.5) = 16.67
30÷(0.4×4.5)=16.67, or approximately 17 panels.
Simplified Solar Panel Home Kit Sizing Tools
Online solar calculators make sizing a system straightforward by considering location, energy usage, and panel efficiency. By entering your address, average monthly electricity usage, and current utility rates, these tools estimate the size of the solar power home system you’ll need and project potential savings.
Cost and Efficiency of Home Solar Electricity
Switching to a solar power home system not only provides long-term cost savings but also offers environmental benefits. As of May 2023, the average cost of grid electricity in the U.S. was 16.5 cents per kWh, whereas solar electricity from a professionally installed system cost between 6 and 8 cents per kWh.
Benefits of Solar Power:
Lower Electricity Bills: Systems sized to cover 100% of electricity usage can eliminate utility costs.
Faster Payback Period: Depending on the cost and available incentives, most homeowners recoup their investment within 7-10 years.
Environmental Impact: Solar systems reduce carbon footprints significantly.Environmental Impact: Solar systems reduce carbon footprints significantly.
The Impact of Appliances on Solar System Sizing
Adding energy-intensive appliances, such as electric vehicles (EVs) or pool heaters, increases your home’s energy demands. This could necessitate a larger panel solar power installation. For example:
· A Level 2 EV charger may require an additional 2-3 kW of solar capacity.
Consider Other Factors That Affect Solar Panel Installation
While electricity consumption, sunlight availability, and panel efficiency are the primary determinants of system size, additional factors can influence the setup:
Roof Space: Ensure there is adequate unshaded roof area to accommodate the required number of panels.
Shading: Nearby trees or structures can reduce efficiency.
Incentives: Federal tax credits and local incentives can offset initial installation costs.
Final thoughts
Sizing a solar power system for home is a multi-step process that requires careful consideration of electricity usage, geographic location, and the efficiency of the selected solar panel home kit. Using tools like the Peak Sun Hours Calculator and consulting local sunlight data can provide more precise estimates. With the right setup, homeowners can transition to clean, renewable energy while maximizing financial and environmental benefits.