Solar energy is transforming the way we utilize power across various fields, playing an especially vital role in providing energy support for off-grid environments like marine applications. As a leader in flexible solar panels, Sungold is dedicated to helping customers gain in-depth product knowledge to make the most suitable choices. This article will guide you through selecting the ideal solar panel for marine environments, enhancing the comfort and efficiency of your voyage.
how to select solar panel for boats?
Selecting the right solar panel for a boat is crucial, as it directly impacts charging efficiency, system compatibility, and long-term usage costs.
Charging Efficiency
Choose a high-power output solar panel to meet the energy needs of deep-cycle marine batteries, ensuring that equipment operates smoothly without the risk of power shortages.
System Compatibility
The panel’s size and installation position must fit the available space on the boat, allowing for easy installation and avoiding installation difficulties or costly modifications.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Marine environments are harsh, so the solar panel should resist corrosion, UV rays, and extreme weather to ensure long service life and reduce maintenance frequency.
Selecting a suitable solar panel will ensure the stability and efficiency of the boat’s power system, enhancing safety and comfort during marine use.
What type of solar panel is best for boats?
When selecting solar panels for marine applications, each type—portable, flexible (including semi-flexible), and rigid—has distinct strengths suited to different boating needs. Understanding the pros and cons of each can help in choosing the right solution for specific marine conditions and power requirements.
Portable Solar Panels
Portable solar panels offer a convenient option for boaters who prefer flexibility and temporary solutions. These panels can be placed in the sunniest spots on the deck or even brought ashore for additional power when anchored.
- Pros: Their easy positioning allows for optimal sunlight capture, and without a permanent installation, they’re a great choice for temporary power needs. Plus, their foldable designs make them space-efficient, especially helpful on boats with limited storage.
- Cons: However, because they’re not fixed, they can be displaced in rough conditions, posing a risk of overboard loss. Weather exposure also means they need to be taken down in poor conditions, limiting their use at times.
- Ideal for: Occasional power boosts when at anchor or docked, without committing to a permanent installation.
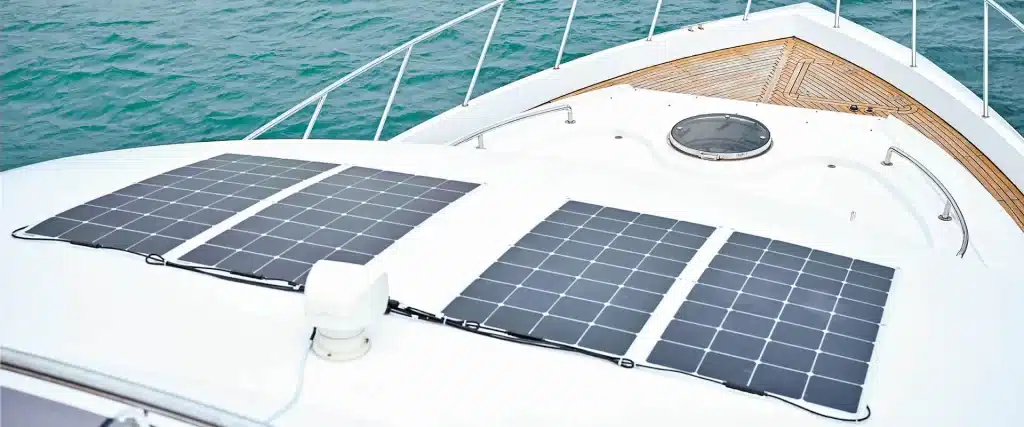
Flexible Solar Panels
For a more integrated setup, flexible solar panels are well-suited to the unique curves and limited spaces of many boats. These panels, lightweight and adaptable, can be mounted on surfaces like biminis or slightly curved decks, offering a balanced solution between efficiency and installation ease.
- Pros: Their versatility and lightness make them easy to mount on various surfaces with minimal impact on weight. Being waterproof and UV-resistant, they’re engineered to withstand marine environments. The flexibility of adhesive or sewn installations further simplifies the setup process.
- Cons: However, they generally provide lower efficiency than rigid panels, which may require more surface area to achieve similar power output. Durability on rough surfaces can also be a concern, as they’re more vulnerable to scratches, especially if walked on.
- Ideal for: Sailboats, small boats, and any vessel with curved or limited flat surfaces that benefit from a more seamless solar solution.

Rigid Solar Panels
For those prioritizing maximum power output and long-term durability, rigid solar panels are an excellent choice. These high-efficiency panels are built to withstand harsh conditions and are often installed on larger boats with ample flat surfaces for secure mounting.
- Pros: Rigid panels are known for their high efficiency, particularly monocrystalline models, which yield more power per square foot. Their durable construction with glass and aluminum frames ensures they handle tough marine conditions well. Additionally, being mounted with a gap for airflow, they stay cooler, enhancing efficiency under direct sun.
- Cons: The downside is their heavier weight and bulkiness, which can add to the load and affect performance on smaller vessels. They also require flat mounting surfaces, limiting where they can be placed and potentially affecting the boat’s aesthetic.
- Ideal for: Larger boats or yachts with stable, spacious surfaces that can accommodate the added weight and structure, where efficiency and durability are the top priorities.
Each type of panel serves specific needs: portable solar panels for adaptability, flexible solar panels for lightweight integration on curved surfaces, and rigid solar panels for top efficiency on larger boats. By balancing these factors, boat owners can select the solar solution that best aligns with their vessel and power requirements.
Best Solar Panels for Boats
For boat owners looking for a reliable and efficient solar power solution, the Sungold TF Series marine solar panel offers some of the best solar panels specifically designed to meet the unique demands of marine environments, ensuring excellent performance and durability on the water.
It’s worth mentioning that Sungold’s newly introduced Anti-Shading Technology has been applied to the TF Series solar panels. This technology effectively addresses the issue of hotspot formation caused by shifting shadows during long voyages, reducing power loss and potential safety hazards. It not only enhances the durability of the solar panels but also ensures a safer user experience.
| Parameter/Model | SG-TF-M2-100W | SG-TF-M2-120W | SG-TF-M2-220W |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Power (W) | 100W | 120W | 220W |
| Open-Circuit Voltage (Voc) | 28.5V | 22.3V | 40.7V |
| Voltage at Maximum Power (Vmp) | 24.4V | 19.1V | 34.8V |
| Current at Maximum Power (Imp) | 4.10A | 6.29A | 6.33A |
| Cell Efficiency (%) | 22.7% | 22.7% | 22.7% |
| Weight (kg) | 1.92kg | 2.26kg | 3.95kg |
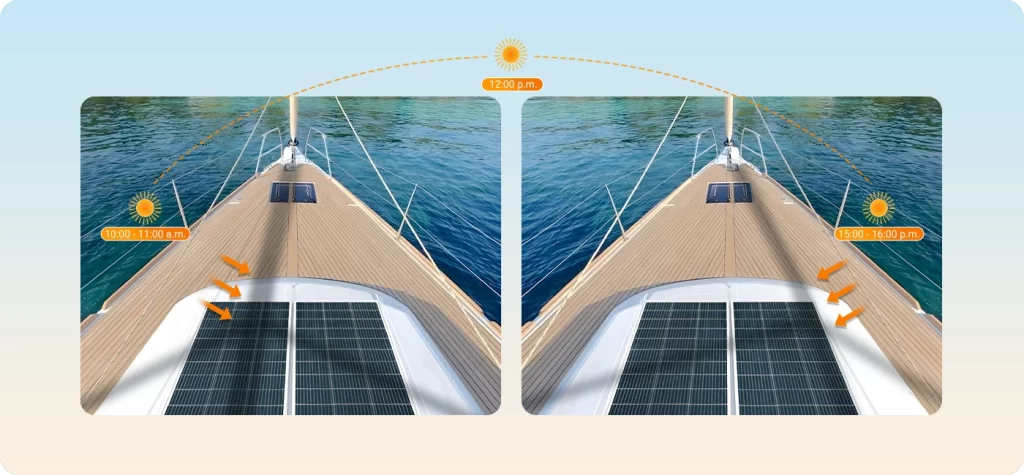
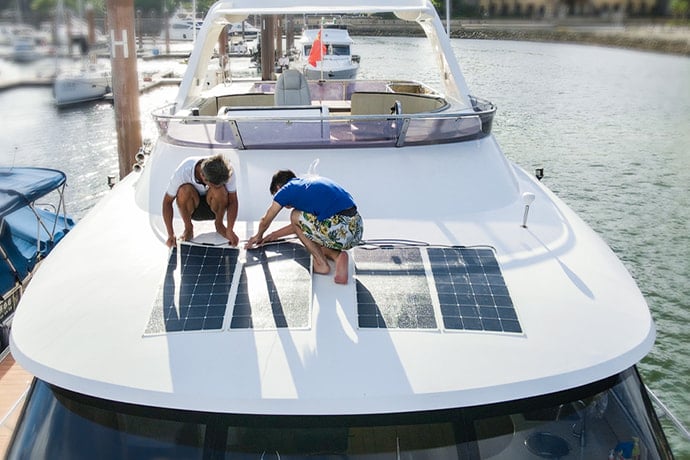
Key Considerations for Installing Solar Panels on Boats
When installing TF Series Solar Panels on boats, several factors must be carefully considered to ensure reliability and durability in marine environments. These panels, cables, and all connections need to meet specific requirements to withstand both the physical stresses and harsh weather conditions encountered at sea.
Durability and Weather Resistance
The solar panels, cables, and connections must be highly resistant to atmospheric elements, especially saltwater, which can cause corrosion. Waterproofing is essential, but the panels must also be robust enough to withstand physical impacts. The panel surface should be strong enough to resist damage from falling objects and bear weight. Ideally, these panels should also be walkable, ensuring that they can handle foot traffic without being damaged.
Weight and Dimensions
The weight and dimensions of the solar panels are critical, as they must be suitable for the available installation space on the boat. If the panel is too heavy, it may negatively impact the boat’s balance or performance. Careful assessment is required to determine the most appropriate size and type based on how much energy is needed and where the panels will be installed.
Type of Solar Panel Based on Usage
The choice of solar panel largely depends on the intended use:
Supplementary Energy Source: If you plan to use the panels as a supplementary power source for occasional use, you can opt for smaller, foldable plug-and-play panels that are easy to install and store when not in use.
Self-Sufficiency for Several Days: For longer trips where self-sufficiency in energy is required, a larger, fixed panel installation may be more suitable. Adjustable panels that can be angled based on the sun’s position will provide optimal energy production over time.
Power Supply and Connectivity
Many plug-and-play panels, such as 12V systems, are designed to work directly with inverters and regulators, allowing the energy generated by the panels to be directly fed into the boat’s electrical system, stored in batteries, or even used to power appliances. This type of system makes it easy to integrate solar power without complex installations.
FAQ
1. Are solar panels on a boat worth it?
Yes, solar panels on a boat are worth it for many boat owners. They provide a sustainable, eco-friendly way to power devices and charge batteries while on the water. Solar panels help reduce the reliance on the boat’s engine or shore power, making them especially useful for longer trips or when anchored in remote locations. They can also extend battery life by providing continuous charging without needing to run a generator, offering convenience and cost savings in the long run.
2. What are marine grade solar panels?
Marine grade solar panels are designed specifically to withstand the harsh conditions of life on the water. They are built to resist corrosion from saltwater, exposure to UV rays, and the physical stresses of constant movement. These panels are made with durable materials and have waterproof ratings (such as IP68) to ensure they can handle the marine environment, making them ideal for boats, yachts, and other marine applications.
3. What size solar panel to keep boat battery charged?
The size of the solar panel needed depends on the power requirements of your boat’s battery system and how much energy you consume. As a general rule:
- For smaller systems, a 100W to 200W panel may be sufficient to maintain a boat battery, especially if the energy demands are low.
- For larger boats or more energy-intensive systems, you might need a 300W to 500W panel or larger.
To determine the exact size, consider factors like battery capacity (amp-hours), daily energy usage, and how much sunlight the boat gets each day.
4. How long does a 100-watt solar panel take to charge a marine battery?
The time it takes for a 100W solar panel to charge a marine battery depends on several factors:
- Battery size (amp-hours)
- Sunlight availability (intensity and duration of sunlight)
- Battery charge level when you start charging
- Efficiency of the solar panel system
On average, under ideal sunlight conditions, a 100W panel can produce about 5-6 amps per hour. If you have a 100Ah battery, it could take approximately 20-24 hours to fully charge a completely depleted battery, considering ideal conditions. However, actual charging time can vary depending on weather and system efficiency.
5. Can a solar panel be too big for a battery?
Technically, a solar panel cannot be “too big” for a battery, as long as the charge controller is appropriately sized to prevent overcharging. The charge controller regulates the flow of energy into the battery, preventing it from being overcharged and damaged. However, having an oversized panel may not be the most efficient choice unless you have very high power needs, as it could result in wasted energy production if the battery is already fully charged or near full.